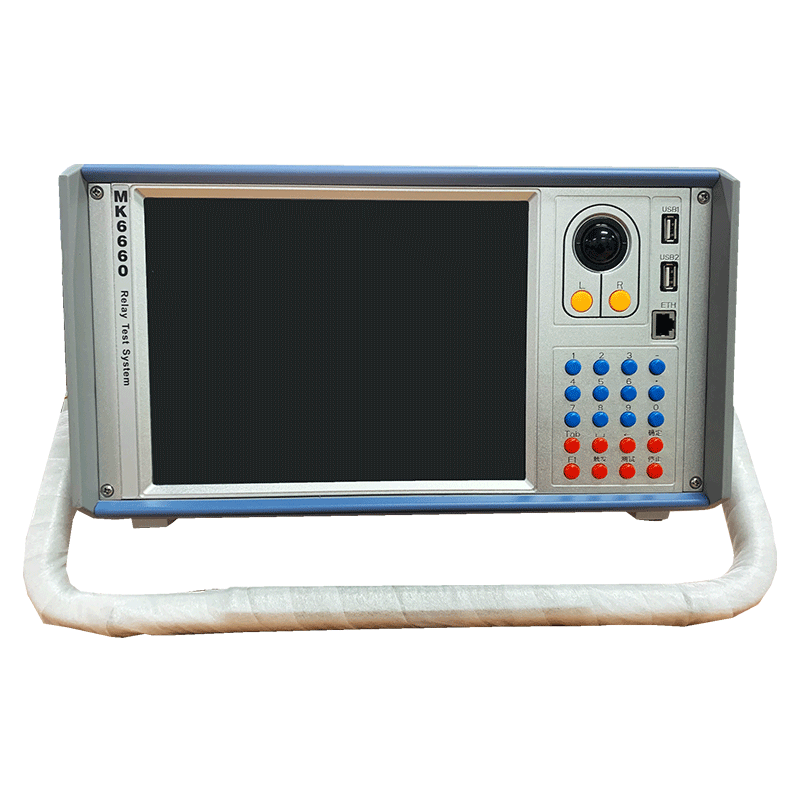

Basic Requirements
In order to complete its task, the relay protection device must meet the four basic requirements of selectivity, speed, sensitivity and reliability in technology. For relay protection acting on relay tripping, four basic requirements shall be met at the same time. For relay protection devices acting on signals and only reflecting abnormal operation conditions, some of these four basic requirements can be reduced.
selectivity
Selectivity means that when the equipment or line in the power system has a short circuit, its relay protection only removes the faulty equipment or line from the power system. When the protection or circuit breaker of the faulty equipment or line refuses to operate, the protection of the adjacent equipment or line shall remove the fault.
Quick action
Quick action refers to that the relay protection device shall be able to remove the fault as soon as possible, so as to reduce the time for equipment and users to operate under high current and low voltage, reduce the damage degree of equipment, and improve the stability of parallel operation of the system.
Faults that must be quickly removed generally include:
Make the bus voltage of the power plant or important users lower than the effective value (generally 0.7 times the rated voltage).
Internal faults of large capacity generators, transformers and motors.
The conductor section of medium and low voltage lines is too small, and delay removal is not allowed to avoid overheating.
Faults that may endanger personal safety and cause strong interference to the communication system.
The fault clearing time includes the action time of protection device and circuit breaker. The action time of general fast protection is 0.04s-0.08s, the fastest can reach 0.01s-0.04s, the tripping time of general circuit breaker is 0.06s-0.15s, and the fastest can reach 0.02s-0.06s.
For relay protection devices that respond to abnormal operation conditions, quick action is generally not required, but signals shall be sent with delay according to selective conditions.
sensitivity
Sensitivity refers to the reaction capability of the protection device when short circuit fault or abnormal operation occurs to electrical equipment or lines within the protected range.
The relay protection that can meet the sensitivity requirements can correctly respond to the action in case of fault within the specified range, regardless of the location and type of the short circuit point and whether the short circuit point has a transition resistance, that is, it is required that it can reliably act not only in case of three-phase short circuit under the maximum operating mode of the system, but also in case of two-phase or single-phase short circuit fault with large transition resistance under the minimum operating mode of the system.
Maximum operation mode of the system: when the end of the protected line is short circuited, the equivalent impedance of the system is the minimum, and the short-circuit current through the protection device is the maximum operation mode;
Minimum system operation mode: under the same short-circuit fault condition, the system equivalent impedance is the maximum, and the short-circuit current through the protection device is the minimum.
The sensitivity of the protection device is measured by the sensitivity coefficient.
reliability
Reliability, including safety and reliability, is the most fundamental requirement for relay protection.
Security: the relay protection is required to be reliable when it is not required to act, that is, no maloperation occurs.
Reliability: the relay protection is required to act reliably when a fault that should act occurs within the specified protection range, that is, it does not refuse to act.
Misoperation and failure of relay protection will bring serious harm to power system.
Even for the same power components, with the development of the power grid, the impact of protection against mal operation and non rejection on the system will also change.
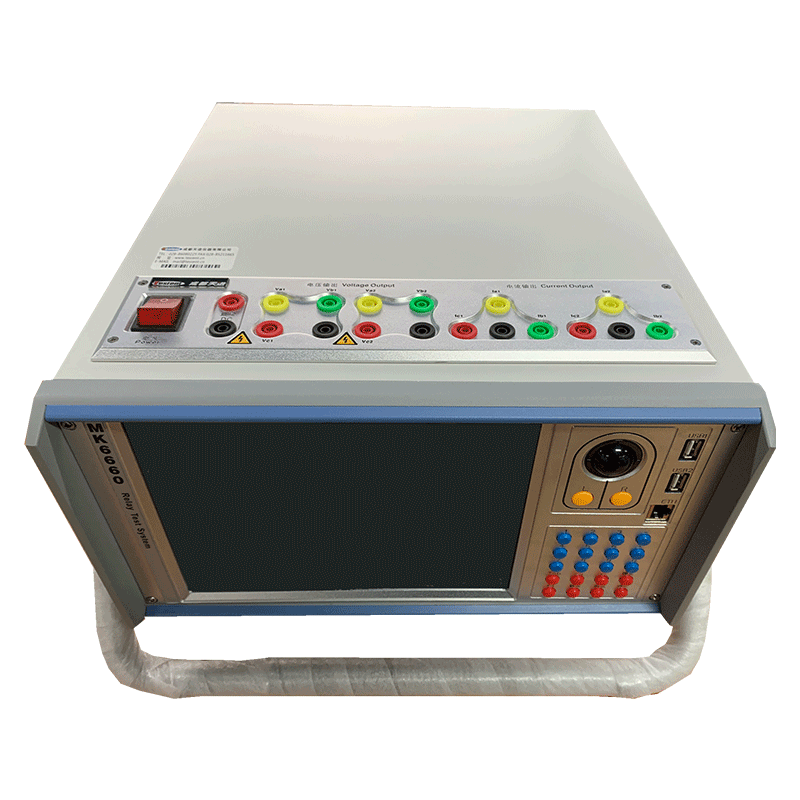


The relay protection device must have the function of correctly distinguishing whether the protected element is in normal operation or has a fault, and whether it is a fault within the protection zone or an external fault. In order to achieve this function, the protection device needs to be composed based on the characteristics of the changes in electrical physical quantities before and after the power system failure.
The main characteristics of power frequency electrical quantity change after power system failure are:
The current increases. In case of short circuit, the current on the electrical equipment and transmission line between the fault point and the power supply will increase from the load current to much more than the load current.
The voltage decreases. When interphase short circuit and ground short circuit faults occur, the interphase voltage or phase voltage value at each point of the system decreases, and the closer to the short circuit point, the lower the voltage.
The phase angle between current and voltage changes. During normal operation, the phase angle between current and voltage is the power factor angle of the load, which is generally about 20 °. In case of three-phase short circuit, the phase angle between current and voltage is determined by the impedance angle of the line, which is generally 60 °~85 °. In case of three-phase short circuit in the opposite direction, the phase angle between current and voltage is 180 °+(60 °~85 °).
The measurement impedance changes. The measured impedance is the ratio of voltage and current at the measuring point (protection installation location). During normal operation, the measured impedance is the load impedance; When the metal short circuit occurs, the measured impedance changes to the line impedance, and the measured impedance decreases significantly after the fault, while the impedance angle increases.
In case of asymmetric short circuit, phase sequence components occur, such as negative sequence current and negative sequence voltage components in case of two-phase and single-phase grounding short circuit; When single-phase grounding occurs, negative sequence and zero sequence current and voltage components appear. These components do not appear during normal operation.
By using the change of electrical quantity during short circuit fault, the relay protection of various principles can be formed.
In addition, in addition to the above protection of power frequency electrical quantity, there is also protection of non power frequency electrical quantity, such as gas protection.
Chengdu Tianjin Instrument Co., Ltd. was established in 2000. For a long time, the company has adhered to people-oriented, adhering to the core values of innovation, integrity and win-win. Consistently pursue high-quality, high-tech professional brand image, and provide customers with better products and services.
In 2001, the M2000 relay protection tester was launched, which took the lead in proposing a three-year free warranty and lifelong maintenance nationwide.
In 2002, the M2000 relay protection tester was approved by the Ministry of Science and Technology, and was supported by the National Innovation Fund for SMEs.
In 2003, it was rated as Chengdu Excellent Entrepreneur.
Since 2004, the company has begun to explore the international market. In 2005, the company has opened the situation in India, Thailand, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia and other countries, exporting more than 70 sets. In the competition with similar manufacturers in the world, it has gained a foothold and won a good international reputation.
In 2006, it was rated as a large taxpayer by Chengdu High tech Zone, and the company's system construction has made great progress.
In 2008, the company completed the research, development, production and sales of MF3000 optical digital relay protection tester, which is the first optical digital relay protection tester in China to pass the IEC61850 protocol test of the State Grid Corporation.
In 2013, the R&D, production and sales of MP3000F digital analog integrated relay protection tester were completed.
In 2015, the research, development, production and sales of TMU-1000 combined unit tester were completed.
Since 2011, the company has ranked first in sales for many years in a row and won the title of large taxpayer in Chengdu High tech Zone.
In 2019, the company successfully launched TS200 relay protection automatic test system and TS210 intelligent remote motor automatic test system.
The company has the ability to produce more than 1230 sets of various types of equipment annually, and has formed economies of scale. The excellent performance and after-sales service of our products have won a good reputation among users.
Zhourong Wang
wang_zr@tesient.cn
